Engine Cooling System: Working Principle, Types, Components & Common Problems
All internal combustion engines are basically heat engines. It transforms the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical power through explosions. But of this energy, only one-third is used to power the vehicle. The rest turns into heat. The fact is, without such a high-performance engine cooling system, your car would actually melt down in the engine. This system works as a thermal shield. It also controls the inside temperature to achieve optimum performance and fuel efficiency. It not only ensures that your engine is not damaged permanently but also increases its life span by far. The essential elements of this critical process are such reliable elements as a good water pump set and engine cooler.
What Is the Engine Cooling System?
The engine cooling system is an elaborate complex of structures that is aimed at controlling thermal energy. Some individuals have assumed that the system cools the engine, but it is more complicated than that. It functions as an accurate thermostat. You should first start your car to have the engine heat up before it can achieve maximum efficiency. An engine that is cold wears out more quickly and is more polluting.
The car cooling system maintains the operating temperature of the engine at the optimum level, independent of the external temperature. It avoids cracking of the engine block, expansion of the pistons, and warping of the cylinder heads. All automobiles of our age, a small hatchback car and a monster tractor alike, depend on this system to live. Without it, the hotness of the combustion would melt the metal parts in a matter of minutes.
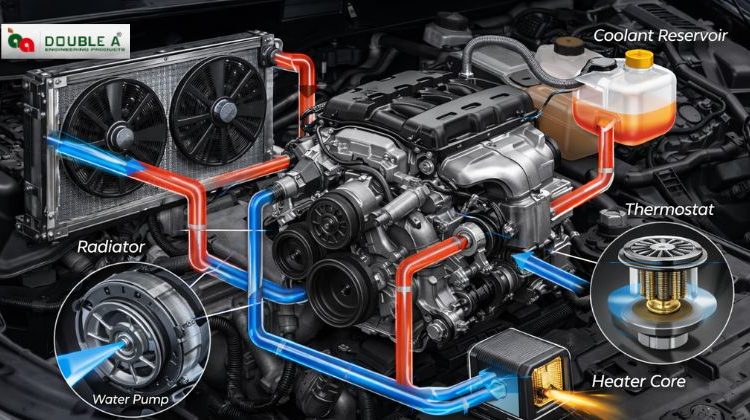
Engine Cooling System Working Principle (How It Works)
The principle of the working of the engine cooling system is based on a simple continuous cycle. It is based on the fact that a specialized liquid is circulated to be used to draw heat out of the core of the engine.
- The Pump Kick starts the Cycle: The engine starts with the water pump assembly. This pump is the heart of this system. It forces liquid coolant into the block and cylinder heads of the engine.
- Heat Absorption: Internal passages known as water jackets cause the coolant to absorb the vast heat generated by the pistons and the valves.
- The Thermostat Performs the role of a Gatekeeper: When the coolant is low, it remains in the engine to aid in warming up the engine. When the liquid has attained a given temperature, the thermostat opens. This enables the hot fluid to pass into the radiator.
- Ejection of Heat to Radiator: The liquid that is hot is introduced to the radiator tubes. The heat is withheld by air that flows through the radiator fins into the atmosphere.
- Re-cooling and Returning: The cooled liquid is made to come out of the radiator and is returned to the pump.
It is this constant flow that maintains your car’s cooling system and your engine’s security.
Types of Engine Cooling Systems
- Air Cooled Engine Cooling System
In an air-cooled engine, the engine block is coated with small metal fins. During the movement of the vehicle, the air passes across these fins and dissipates heat. The system is highly portable and easy to maintain as it does not have any radiators or hoses. But it is not as effective with heavy-duty machines. This is mostly present in motorcycles, lawnmowers, and the older classic cars. - Cooling System, Liquid-Cooled Engine
This is the norm of contemporary automotive engineering. It incorporates a combination of water and chemical antifreeze (coolant). The boiling point and freezing point of this liquid are higher than those of plain water. This system offers better temperature controls for commercial vehicles and tractors. It makes sure that the engine remains at a steady temperature even during extreme stop-and-go traffic. - Oil-Based Cooling System
The high-performance engines usually produced more heat than water could handle on its own. These machines are supplied with an engine oil cooler. The oil cooler pump circulates the engine oil in a special heat exchanger. This keeps the oil thick enough so that it lubricates the moving parts. When the oil is overheated, it will be thin like water and will not safeguard the engine.
What Are the 4 Main Parts of the Cooling System?
Any good car cooling system is based on four key components to remain operational:
- Radiator: It is the main heat exchanger. It is used on the front side of the car in order to receive the maximum amount of air. It is its duty to convert hot coolant to cool liquid.
- Water Pump: it is the mechanical heart. The coolant is pumped out at high pressure with a high-quality water pump assembly to provide the coolant to all areas of the engine block.
- Thermostat: It is a small valve that acts as the brain. It determines the temperature of the coolant and when it is time to go through the radiator to cool it.
- Cooling Fan: An electric fan is used to supply important airflow in the car when it is not in motion. It draws air over the radiator fins when the car is not on high speed to get natural wind.
Components and Functions of an Engine Cooling System
| Component | Primary Function |
| Radiator | Removes the heat generated by the hot coolant into the atmosphere. |
| Water Pump Assembly | Takes the liquid coolant up and down in the engine and radiator. |
| Thermostat Valve | Opens and closes to keep the engine temperature at its best. |
| Electric Cooling Fan | Gathers air inside the radiator to accelerate low-speed cooling. |
| Oil Cooler Pump | Maintains the oil in the engine at the right level to lubricate the important parts. |
| Expansion Tank | This adds a coolant reservoir with an increase in heat. |
| Pressure Cap | Helps to maintain the pressure in the system to increase the boiling point of the coolant. |
What Happens If Your Engine Overheats?
When your engine overheats, you know it will be expensive and fast. The high temperature causes the metal components of the engine to be extended beyond the design limits. You could have a blown head gasket that will cause the coolant to spill over into the combustion chamber. This causes whitening of the smoke in the exhaust, and the engine is ruined.
The worst-case is that the engine can seize. This is because the pistons have stretched to an extent that they have joined the walls of the cylinder. Fuel efficiency is also eliminated by overheating. The engine has problems keeping time, burns more fuel, and generates less power. A failure in the engine cooler will reduce a mere trip into a complete loss of the vehicle.
Common Engine Cooling System Problems
- Coolant Leakage: It was the leading cause of overheating. The problem may occur in the radiator, the hoses, or the water pump assembly and cause a leak.
- Malfunctioning Thermostat: In the case of a stuck thermostat in the closed position, the radiator is not accessible to the coolant. It will take minutes to overheat the engine.
- Radiator Clogging: Radiator in the long run, becomes blocked by dirt and rust in the tiny tubes of the radiator. This prevents the spillage of the coolant.
- Electric Cooling Fan Failure: When the fan motor malfunctions, your engine will overheat, particularly when you are stuck in traffic.
- Malfunctioning of Oil Cooler Pump: This results in thin, inefficient engine oil, which results in untimely wearing of internal bearings and camshaft of the engine.
Signs Your Car Cooling System Needs Maintenance
Be alert and look out for these red flags so that you are not faced with a huge bill of repair:
- The dashboard thermometer has gone to the red zone.
- The green Low Coolant light or the check engine light comes on your dashboard.
- You can even see the steam/smoke coming out of the sides of the hood.
- You observe the sweet-smelling, brightly colored puddles (green, orange, or pink) beneath your parked car.
- There is a grinding or whining sound that is heard in the water pump assembly.
How to Maintain an Engine Cooling System
Preventive maintenance is less expensive than an engine rebuild is always. Check the levels of coolants frequently, make sure that the fluid is full and clean. The engine cooling system should be flushed every two years to eliminate internal rust and debris. Change your water pump assembly at the prescribed durations, that is, every 60,000 to 100,000 miles. Always spend good money on an oil cooler pump and high-quality coolant so that you can save your engine from its delicate internal parts due to corrosion.
Difference Between Engine Cooling System and Oil Cooling System
| Feature | Engine Cooling System | Oil Cooling System |
| Primary Purpose | Cools the engine block and the cylinder heads. | Cools the lubricating oil to uphold viscosity. |
| Cooling Medium | Liquid Antifreeze/WaterMix. | Engine Oil. |
| Key Component | Radiator and Water Pump Assembly. | Engine Cooler and Oil Cooler Pump. |
FAQs
Q1. What is the frequency of changing the coolant?
Ans: To avert internal corrosion, most manufacturers suggest a complete system flush every 30,000 to 50,000 miles.
Q2. Is it possible to run a car without a cooling fan?
Ans: However, only on highways with strong winds. Without an electric cooling fan, the engine will overheat almost instantly in road traffic in the city.
Q3. Do all engines need cooling with oil?
Ans: Heavy-duty tractors, commercial vehicles, and turbocharged cars that work under high pressure over extended periods of time require it.
Q4. What is the purpose of the pressure cap of an engine cooling system?
Ans: The cap makes the system strained. This increases the boiling point of the coolant, which therefore has the capacity of retaining more heat without changing into steam.
Q5. Why does the car’s cooling system lose fluid without any visible leak?
Ans: This fluid may be leaking internally due to a blown head gasket or evaporating due to a defective pressure cap. It should be checked over at once.
Conclusion
Vehicle longevity depends on a well-developed engine cooling system. It provides efficiency of your machine, fuel efficiency, and prevents it from ending up in the scrap yard. Quality parts eliminate unexpected failure and save you a lot of money. Makhija International is a company that deals in the production of the best water pump assemblies and oil cooler pumps. Our 3D scanning and CNC production are designed to provide your engine with the ability to operate in cool conditions, even in the harshest industrial environments.





